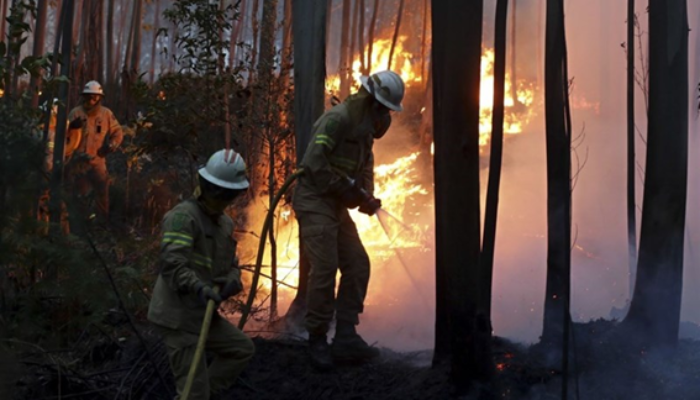
In the last decades, the strength of climate change has been evident across the globe in many weather and climate extremes occurrences, including heatwaves and droughts. Those events are involved in all fire stages and influence all aspects of the fire regime.
The use of Machine Learning in fire research is rapidly advancing, not only for events detection and mapping but also for fire susceptibility and risk assessment, fuels characterisation, fire weather and climate change, fire impacts and fire management. These techniques are generally emerging as a new paradigm in geosciences: they are capable of discovering the hidden relationships between the hazard events and the environmental, meteorological and anthropogenic complex drivers allowing us to make predictions, in terms of probabilistic outputs.