De Novo assembly
Long sequencing reads (several tens of kb) greatly facilitate de novo genome assembly and variants phasing. It also allows the analysis of structural variants (insertions, deletions, repetitions of regions of several tens of nucleotides) which are invisible with short read sequencing data.
De novo assembly has successfully been applied to bacteria, insects, plants, mammals, and more.

Variant detection
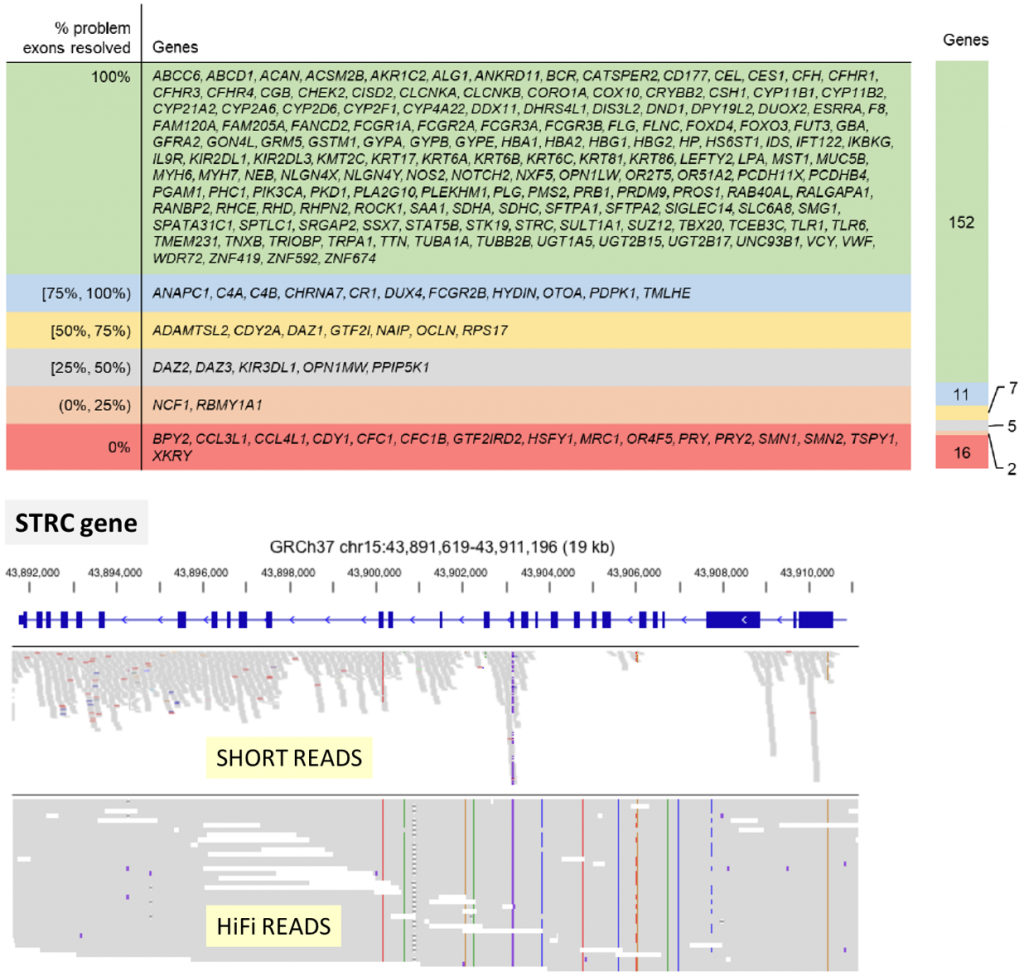
HiFi reads length, accuracy, and uniformity open access to genomic regions impossible to analyze with short reads sequencing.
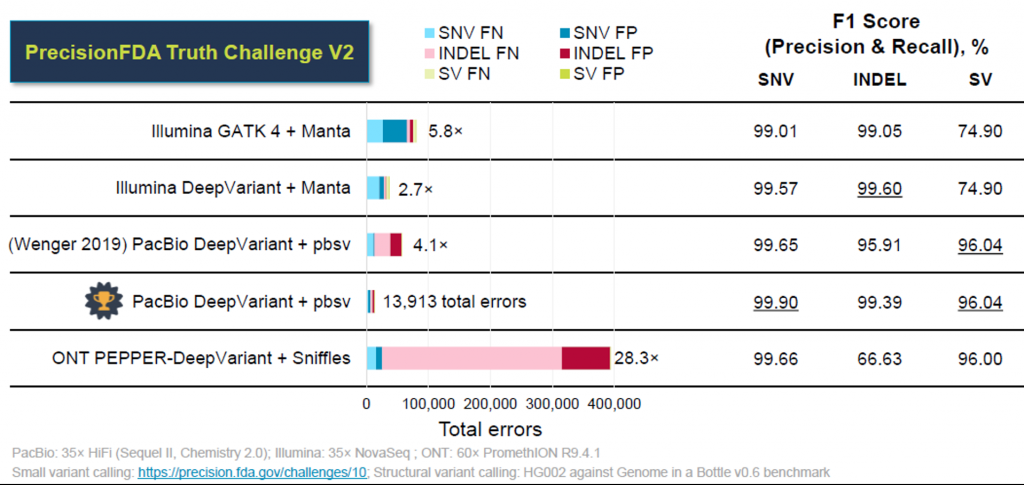
The Truth Challenge V2 from the FDA, aimed at comparing technologies for calling variants in difficult-to-map regions, revealed that HiFi reads can outperform short read sequencing.
Epigenetics
SMRT sequencing can detect some DNA modifications by design, i.e. without the need for DNA treatment or special library preparation
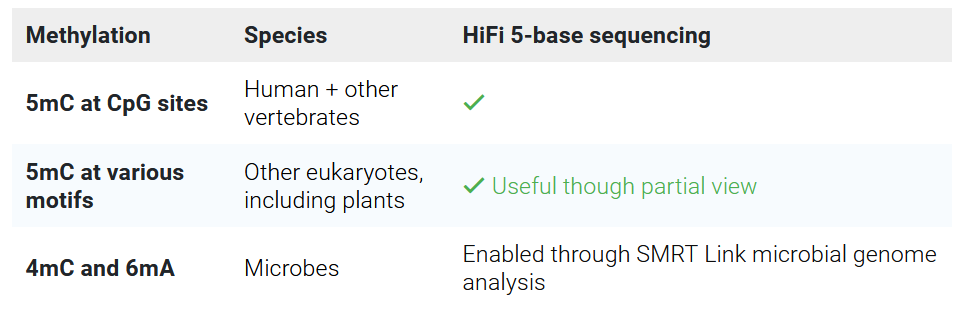
More information about epigenetics applications can be found on PacBio’s website
Full-Length RNA sequencing
For Pacific Biosciences sequencing, full-Length RNA sequencing (from 5′ cap to 3′ poly A tail) is called ISOseq. The high-quality sequences obtained give a qualitative view of transcript isoform diversity, even for very short exons.
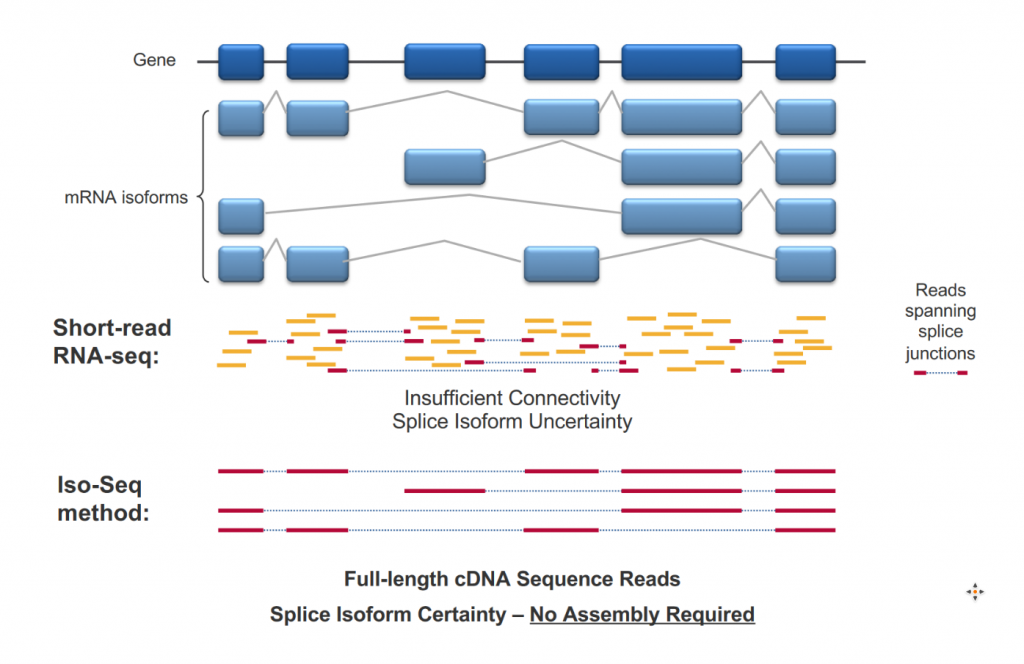
The sequencing saturation offered by PacBio sequencing is so far not sufficient for standard transcriptome profiling. It is therefore a qualitative approach only. Quantitative approaches are under development (Pacific Biosciences and Oxford Nanopore) but this is not fully supported by GTF yet.
The main applications are:
• Genome annotation
• New gene, or transcript isoform discovery
Along the same line, methods are being developed for performing ISOseq at the single cell level (MAS-Seq). The double stranded full-length cDNA, amplified as part of the 10X genomics single cell RNAseq procedure, is the template for ISOseq library preparation.
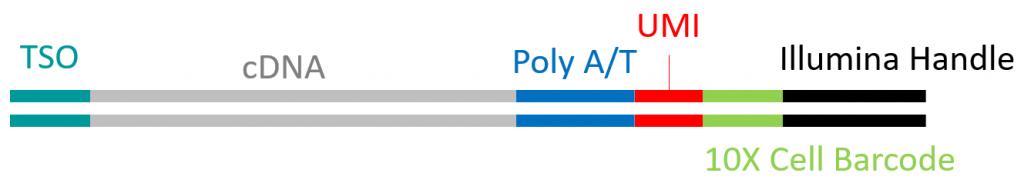
Typical structure of a single cell derived 10X full length double strand cDNA
Amplicon sequencing
Another benefit of long read sequencing, of particular interest for amplicon sequencing, lies in the fact that variants can easily be phased (see below). This information is key for applications such as HLA typing of VDJ sequencing for instance.
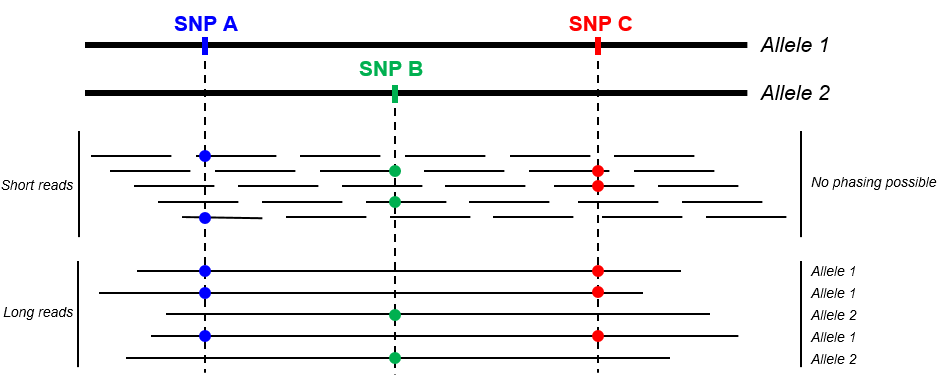
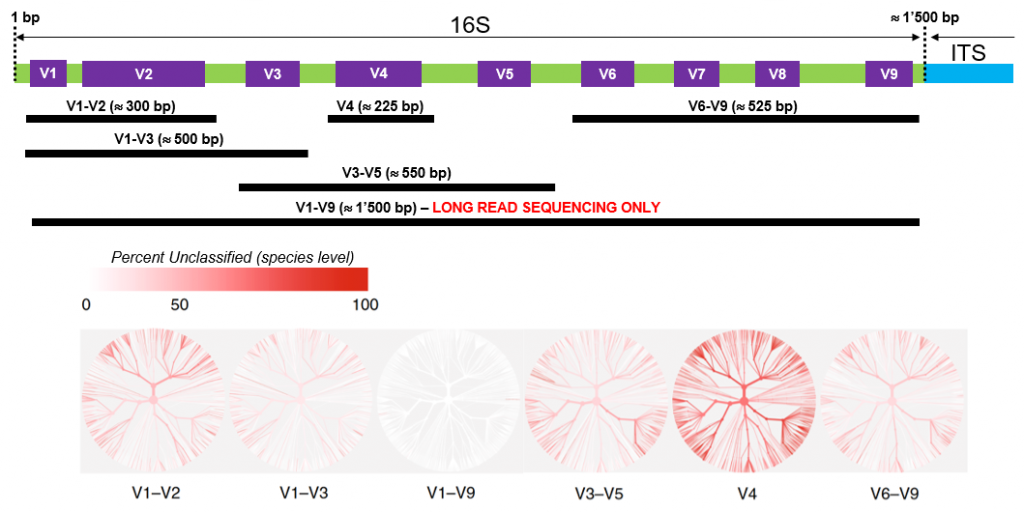
Full length 16S sequencing is another key application for high accuracy long read amplicon sequencing. Getting access to the full 1.5 kb 16S sequence indeed greatly improves sensitivity and precision compared to standard short variable region analysis (see figure below), potentially “providing taxonomic resolution of bacterial communities at species and strain level”.
GTF can provide primers for “full-length” bacterial 16S amplification (see Practical Informations)