- Regulation and function of a polarly localized lignin barrier in the exodermis
- Concepcion Manzano,
- Kevin W. Morimoto,
- Lidor Shaar-Moshe,
- G. Alex Mason,
- Alex Cantó-Pastor,
- Mona Gouran,
- Damien De Bellis,
- Robertas Ursache,
- Kaisa Kajala,
- Neelima Sinha,
- Julia Bailey-Serres,
- Niko Geldner,
- J. Carlos del Pozo &
- Siobhan M. Brady
Nature Plants (2024)
Abstract
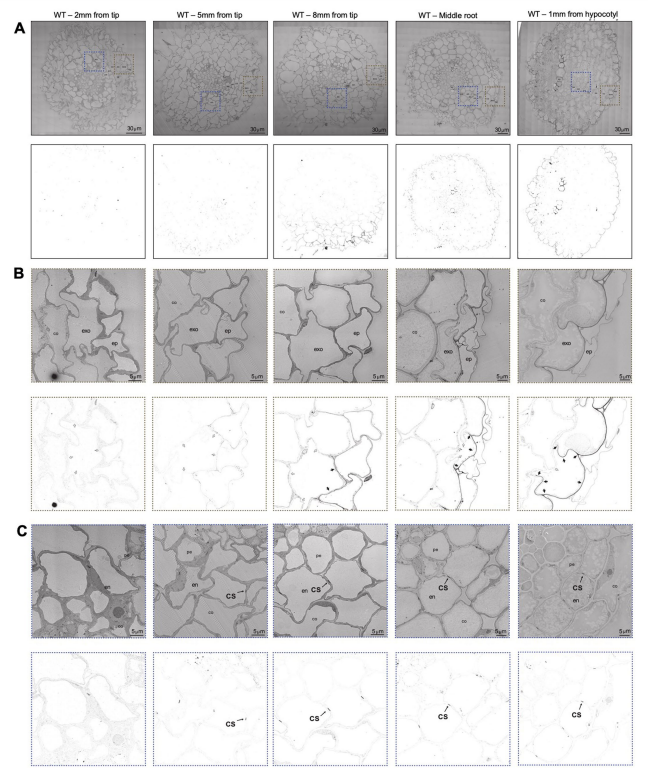
Multicellular organisms control environmental interactions through specialized barriers in specific cell types. A conserved barrier in plant roots is the endodermal Casparian strip (CS), a ring-like structure made of polymerized lignin that seals the endodermal apoplastic space. Most angiosperms have another root cell type, the exodermis, that is reported to form a barrier. Our understanding of exodermal developmental and molecular regulation and function is limited as this cell type is absent from Arabidopsis thaliana. We demonstrate that in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), the exodermis does not form a CS. Instead, it forms a polar lignin cap (PLC) with equivalent barrier function to the endodermal CS but distinct genetic control. Repression of the exodermal PLC in inner cortical layers is conferred by the SlSCZ and SlEXO1 transcription factors, and these two factors genetically interact to control its polar deposition. Several target genes that act downstream of SlSCZ and SlEXO1 in the exodermis are identified. Although the exodermis and endodermis produce barriers that restrict mineral ion uptake, the exodermal PLC is unable to fully compensate for the lack of a CS. The presence of distinct lignin structures acting as apoplastic barriers has exciting implications for a root’s response to abiotic and biotic stimuli.