Enhancing Bone Marrow Evaluation with digital and computation hematopathology
MarrowQuant 2.0 (Sarkis et.al, 2023)
We have developed MarrowQuant to accurately assess bone marrow (BM) cellularity in murine and human (MarrowQuant 2.0) tissues, as well as to quantify BM adipocyte size through the associated StarDist for adipocytes plugin .Developed and validated within QuPath software, MarrowQuant 2.0 quantifies 5 distinct human BM compartments, including bone, hematopoietic, adipocytic, and interstitial/microvasculature areas. Our innovative algorithm, in addition to utilizing machine learning-based StarDist, ensures precise instance segmentation of individual adipocytes. With robust BM compartment segmentation and high correlation to hematopathologists’ estimations, MarrowQuant 2.0 is a reliable tool for BM cellularity assessment. New projects associated to this branch of the lab are exploring novel morphological markers in BM stromal components as potential biomarkers in the context of hematological cancers. Thanks to our long-standing collaboration with the EPFL Bioimaging & Optics platform, the Center for Bioimaging, and the CHUV Institute of Pathology, new lab members participate in developing the future of computational hematopathology.
Hematon Units: an access point to elucidate human bone marrow stromal niche heterogeneity
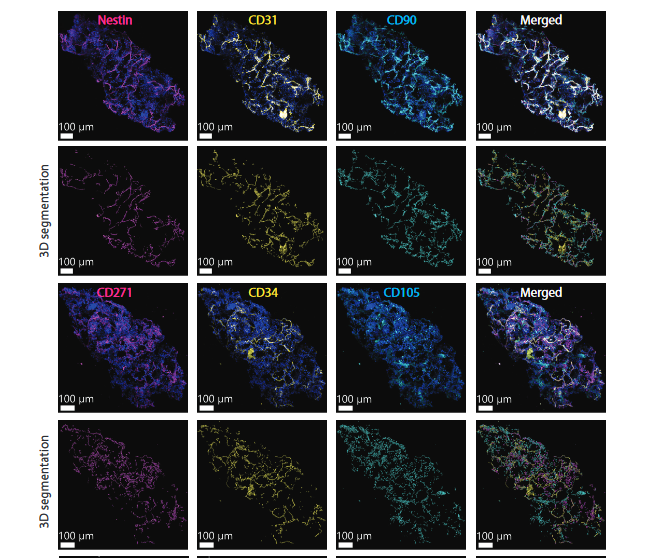
New lab members can also join our innovative study using Hematon Units (HU) to analyze the in-situ heterogeneity of the BM niche. Our advanced technology and close collaboration with the CHUV Hematology Service allow us to assess the relative stromal cell composition and spatial organization in full BM tissue specimens. With a panel of fifteen validated human BM stromal markers, we are unveiling the co-expression of stromal cell surface markers and their micro-anatomic localization, as well as exploring the potential of HUs as an ex vivo model for studying the heterogeneity of the human BM stroma in regenerative medicine and hematopoiesis.