Subseasonal prediction of compound extremes driven by the stratosphere.
SNSF grant “STRATcompound” 2025 – 2029.
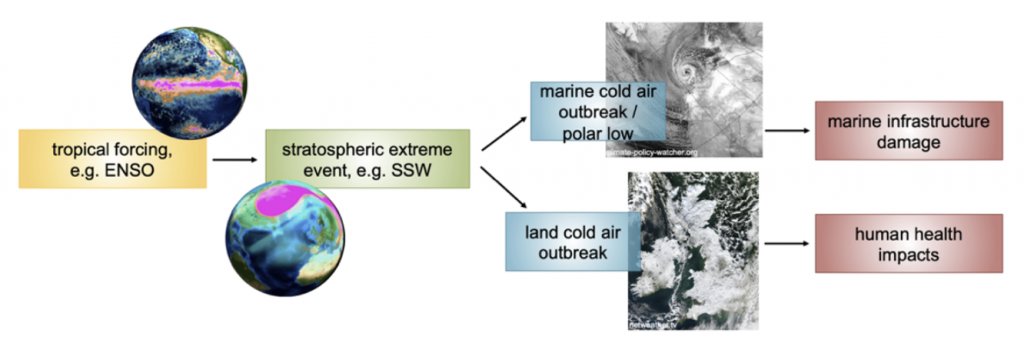
Extreme weather and climate events such as hot or cold spells or precipitation extremes can have severe impacts, for example for human health, ecosystems, agriculture, and infrastructure. When such weather extremes occur as compound events, for example when a common driver leads to a wide range of different impacts, or if multiple drivers amplify an impact, then the damages can be amplified. It is therefore crucial to anticipate such hazards and their impacts as long as possible in advance. While many compound extremes will increase in frequency or severity in a changing climate, it is not yet understood if they can be anticipated on the timescales that allow for emergency preparation, that is, several weeks in advance, so-called subseasonal timescales. There is indeed potential for subseasonal prediction if at least one of the compounding factors is remotely driven. An important driver of compound extremes is the stratosphere, which can trigger surface weather extremes. These extremes can lead to a variety of hazards that occur concurrently or consecutively in a cascading manner, but they have not yet been considered in a compound event framework. The focus of the here proposed research lies in identifying compound extremes related to precursors in the extratropical stratosphere. The envisaged hazards include storm series that can lead to excessive precipitation, temperature extremes such as marine and land cold air outbreaks and hot spells, compound extremes modulated by the tropics and driven by the stratosphere, as well as cryospheric extremes such as snow droughts and permafrost thawing. Both dynamical and artificial intelligence-based subseasonal prediction models will be used to identify the forecast skill of compound extremes and to isolate the role of the stratosphere. Sensitivity studies will be performed to attribute the extremes and to understand the links between the drivers and the compound extremes, to identify the origins of predictability and to understand compound extremes driven by the stratosphere in a changing climate.