Exploring the genetic and metabolic foundations of sleep
At the Vassalli Lab, we investigate the intricate genetic and molecular mechanisms that govern sleep, a vital yet functionally enigmatic biological process. Our research focuses on understanding how the brain regulates sleep and wakefulness, the mechanisms behind sleep disorders like narcolepsy, and ways to improve wakefulness and cognitive function. By studying the Hypocretin/Orexin system, we aim to uncover how sleep patterns are maintained, what goes wrong in sleep disorders, and how targeted therapies could restore normal function.
Our aims
1) Understanding Sleep/Wake Rhythms
We explore how the brain maintains stable sleep and wake states, particularly through the Hypocretin/Orexin system:
- Neural Circuitry of Sleep: Investigating how Hypocretin/Orexin and its receptors regulate wakefulness, non-REM sleep, and REM sleep to ensure smooth transitions and stable sleep cycles.
- Sleep Disorders & Neuromodulation: Examining how dysfunction in this system leads to disorders such as Narcolepsy Type 1 (NT1) and Type 2 (NT2), ADHD, addiction, and OCD.
- Brain Imaging & Circuit Mapping: Utilizing advanced brain-clearing techniques to study the functional neuroanatomy of the Hypocretin/Orexin network.
2) Unraveling the Hypocretin/Orexin circuit: Orexin-to-Dopamine neurotransmission
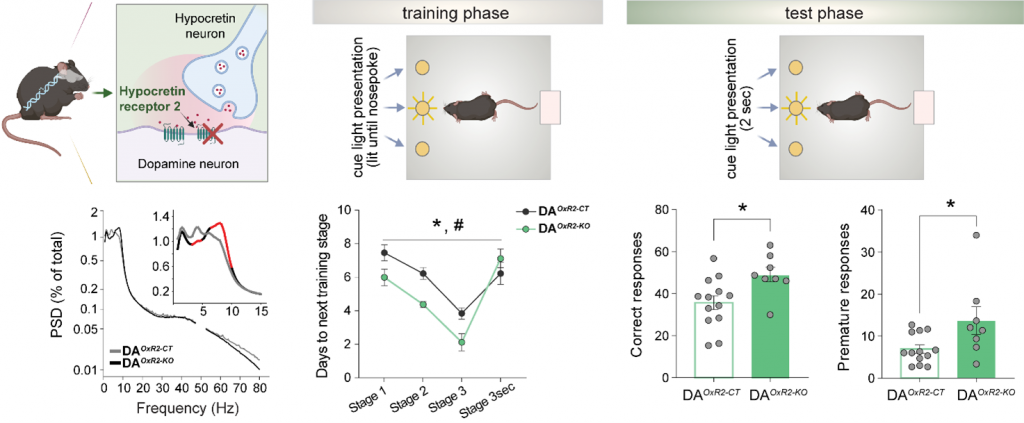
2.1 Inactivation of hypocretin receptor-2 signaling in dopaminergic neurons induces hyperarousal and enhanced cognition but impaired inhibitory control
Hypocretin/Orexin (HCRT/OX) and dopamine (DA) are both key effectors of salience processing, reward and stress-related behaviors,
and motivational states. Yet their respective roles and interactions are poorly delineated. We inactivated HCRT-to-DA connectivity
by genetic disruption of Hypocretin receptor-1 (Hcrtr1/Ox1R), Hypocretin receptor-2 (Hcrtr2/Ox2R), or both receptors (Hcrtr1&2) in DA neurons and
analyzed the consequences on vigilance states, brain oscillations and cognitive performance in freely behaving mice. Unexpectedly,
loss of Hcrtr2, but not Hcrtr1, nor Hcrtr1&2, induced a dramatic increase in theta (7–11 Hz) EEG activity in both wake and rapid-eye-movement sleep (REMS). DAHcrtr2-KO mice spent more time in an active (theta activity-enriched) waking substate, and exhibited prolonged REMS. Additionally, both wake and REMS displayed enhanced theta-gamma
phase-amplitude coupling. Baseline waking EEG of DAHcrtr2-KO mice exhibited diminished infra-theta, but increased theta power, two hallmarks of EEG hyperarousal, uncoupled from locomotor activity. Upon exposure
to novel, either rewarding or stress-inducing environments, DAHcrtr2-KO mice featured more pronounced waking theta and
fast-gamma (52–80 Hz) EEG activity surges compared to controls, further suggesting increased alertness. In an operant conditioning paradigm, DAHcrtr2-KO mice manifest faster learning and higher attentional skills under increasingly demanding task contingencies. The mice concurrently displayed maladaptive patterns of reward-seeking, with behavioral indices of enhanced impulsivity and compulsivity. None of the
EEG changes observed in DAHcrtr2-KO mice were seen in DAHcrtr1-KO mice. Our findings establish a clear genetically-defined link between monosynaptic HCRT-to-DA neurotransmission and theta oscillations, with a novel role of HCRTR2/OX2R in theta-gamma cross-frequency coupling, attentional processes, and executive functions, relevant to disorders including narcolepsy, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and Parkinson’s disease.
Inactivation of hypocretin receptor-2 signaling in dopaminergic neurons induces hyperarousal and enhanced cognition but impaired inhibitory control
Contributors: Mojtaba Bandarabadi; Sha Li; Lea Aeschlimann; Giulia Colombo; Stamatina Tzanoulinou; Mehdi Tafti; Andrea Becchetti; Benjamin Boutrel; Anne Vassalli
Molecular Psychiatry – 2024-02 | Journal article
DOI: 10.1038/s41380-023-02329-z
2.2 Divergent modulation of dopaminergic neurons by hypocretin/orexin receptors-1 and -2 shapes dopaminergic cell activity and socio-emotional behavior
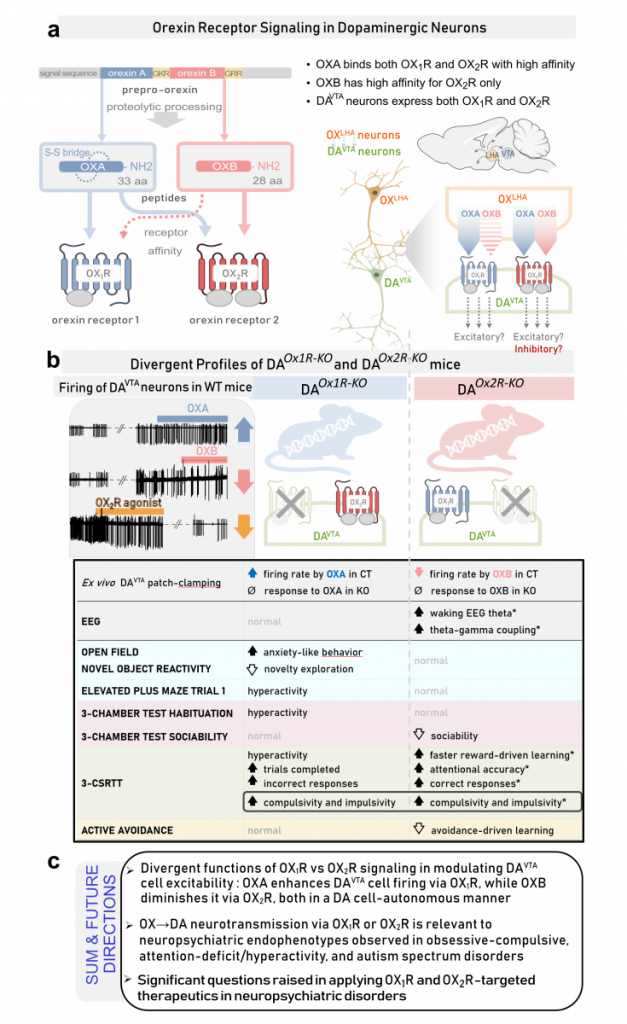
Many neuropsychiatric disorders involve dysregulation of the dopaminergic (DA) input to the forebrain. Of particular relevance are DA projections stemming from the midbrain ventral tegmental area (VTA). A key neuromodulatory influence onto DAVTA neurons arises from lateral hypothalamic area hypocretin/orexin (OX) neurons. Despite being a major input, the differential action of orexin peptides A and B (OXA and OXB) on orexin receptors 1 and 2 in DA cells is poorly understood. We recently identified profoundly divergent functions of OX1R vs OX2R in DA cells in regulating sleep/wake architecture, brain oscillations and cognitive behaviors. OX2R, but not OX1R, loss dramatically increased time in EEG theta-rich (alert) wakefulness, reward-driven learning and attentional skills, but impaired inhibitory control.
Using our genetically engineered mice whose DA cells selectively lack OX input via Hcrtr1 (DAOx1R-KO) or Hcrtr2 (DAOx2R-KO), we assessed intrinsic excitability and electrophysiological responses of DAVTA neurons and evaluated behavioral phenotypes across multiple domains.
We uncover previously unrecognized effects of OX peptides on DAVTA cell response. In WT and control mice, we show that while OXA enhances, OXB diminishes DAVTA neuronal excitability. OX1R-deficient DA cells lose OXA responding and OX2R-deficient DA cells lose OXB responding. DA Ox1R loss generates anxiety-like behavior and context-dependent hyperactivity. In contrast, OX2R loss decreases sociability and, despite exhibiting enhanced reward-driven learning, mice show highly compromised aversion-driven learning.
CONCLUSIONS: We evidence strikingly distinct functions of OX1R vs OX2R signaling in modulating the intrinsic excitability of DAVTA neurons and influencing DA-related behaviors. These data implicate OX→DA signaling pathways in neuropsychiatric endophenotypes relevant to obsessive-compulsive, attention-deficit/hyperactivity, and autism spectrum disorders, and raise important considerations for the development of OXR-targeted therapeutics.
- Divergent modulation of dopaminergic neurons by hypocretin/orexin receptors-1 and -2 shapes dopaminergic cell activity and socio-emotional behavior
- Stamatina Tzanoulinou, Simone Astori, Laura Clara Grandi, Francesca Gullo, Richie Kalusivikako, Simran Rai, Galina Limorenko, Mehdi Tafti, Andrea Becchetti, and Anne Vassalli
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.02.14.638329v2
3) Unraveling the Causes of Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is believed to arise from complex neuro-immune interactions and epigenetic factors. Our research aims to:
- Investigate the Epigenetic Hypothesis: We study how genetic and environmental factors contribute to narcolepsy, with the goal of developing the first disease-modifying therapy.
- Develop Humanized Mouse Models: We engineered a mouse model where the mouse Hcrt gene is replaced by the human HCRT gene, alongside the narcolepsy-associated HLA allele DQB10602/DQA10102 (DQ6), to study the disease mechanisms and test potential treatments.
- InnoSuisse Grant & Therapeutic Innovations: Our InnoSuisse-supported research aims to translate these findings into novel epigenetic therapies for narcolepsy.


4) Enhancing Wakefulness and Cognitive Performance
We study how wakefulness-promoting drugs impact brain activity and cognitive function:
- Pharmacological Enhancement of Wakefulness: Investigating how medications like Solriamfetol (Sunosi®) and Modafinil improve wakefulness in people with hypersomnia and whether they can enhance cognition in healthy individuals.
- Electrophysiological Markers of Alertness: Using EEG and deep-brain recordings, we analyze how these drugs affect brain wave patterns associated with attention, learning, and memory.
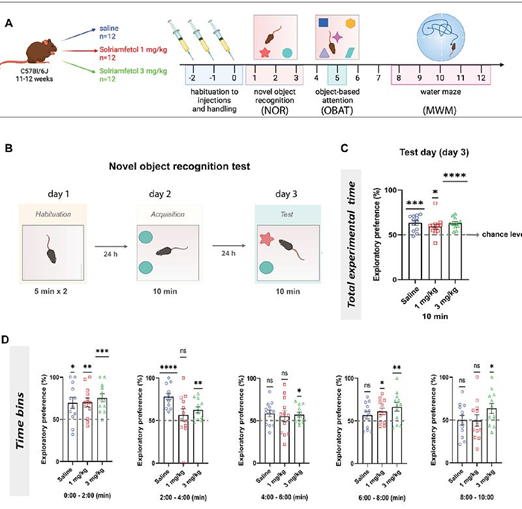
- Cognitive Effects of Solriamfetol: Our studies show that low doses improve attention and memory in mice, linked to increased EEG gamma activity, a marker of cognitive engagement.
Recent findings (Haddar et al., 2025) demonstrate that Solriamfetol enhances cognitive performance in wild-type mice, supporting its potential as both a therapeutic and cognitive enhancer.
by Meriem Haddar, Stamatina Tzanoulinou, Li Yuan Chen, Mehdi Tafti, and Anne Vassalli
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.01.02.631072v1
DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.02.631072
Research
Our research builds on the foundations laid by the work led by Prof. Mehdi Tafti, see details here
The work led by Prof. Mehdi Tafti revealed that sleep traits—such as duration, distribution, and distinct electroencephalographic (EEG) features—are under genetic control in both humans and animal models. Using inbred mouse models, this work pioneered the identification of single genes influencing quantitative sleep EEG traits. For instance, it uncovered that the theta frequency of paradoxical sleep is highly heritable, and linked to the Acads gene, a key player in fatty acid metabolism. Similarly, it identified Rarb, a gene involved in vitamin A signaling, as a determinant of slow-wave activity (or power in delta oscillatory range, 1-4 Hz) during non-REM sleep. Work focusing on unraveling the genetic architecture of sleep need—a homeostatically regulated process by which sleep loss triggers compensatory recovery sleep— identified Homer1a as a molecular marker of prolonged wakefulness. Additionally, we developed an innovative in vitro “sleep in a dish” model, allowing us to study electrophysiological, transcriptomic, and metabolic correlates of sleep and wakefulness, and to explore how sustained wakefulness impacts membrane metabolism.
Orexin system
Anne Vassalli lab conducts research into the orexin system and its involvement in sleep disorders such as narcolepsy and cataplexy. This research focuses on understanding the role of orexin neurons in the hypothalamus and how their dysfunction can lead to these disorders.
What are the main definitions?
Orexin (Hypocretin)
Orexin refers to a set of neuropeptides produced by neurons in the hypothalamus. These peptides play a critical role in regulating wakefulness, arousal, and appetite. Orexin neurons send signals to various brain regions to help maintain alertness and prevent the sudden onset of sleep during the day. Dysfunction or loss of these neurons is strongly linked to the sleep disorder narcolepsy.
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a chronic sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep. It is often caused by a loss of orexin-producing neurons in the hypothalamus. People with narcolepsy may struggle to stay awake during normal waking hours, and their sleep cycles are often fragmented. The most severe form, narcolepsy type 1, is associated with a near-total absence of orexin neurons.
Cataplexy
Cataplexy is a sudden and temporary loss of muscle tone, often triggered by strong emotions such as laughter, excitement, or anger. This condition is commonly associated with narcolepsy type 1. During a cataplectic episode, a person may collapse or experience muscle weakness but remain fully conscious. Cataplexy occurs when the brain suddenly loses its ability to regulate muscle control, likely due to the disruption of orexin signaling.
How do we study it?
The lab studies the orexin system, focusing on how orexin neurons contribute to maintaining stable wakefulness and preventing inappropriate transitions between sleep and wake states, as seen in narcolepsy and cataplexy.
By manipulating orexin neurons in mouse models, we explore:
- How lack of orexin leads to narcoleptic symptoms.
- The neural circuits that link emotional stimuli to cataplexy.
- The development of potential treatments aimed at restoring orexin function or compensating for its loss.
This research has implications for understanding the neural basis of sleep disorders and finding novel therapeutic strategies for people with narcolepsy and related conditions.
Epigenetics
Our lab investigates the epigenetic silencing of the orexin gene and potential methods to reverse this silencing as a way to understand and treat disorders like narcolepsy, where orexin production is disrupted. This research focuses on how changes in gene expression—without altering the underlying DNA sequence—can affect the function of orexin neurons.
Epigenetic Silencing of the Orexin Gene
Epigenetic silencing refers to the process by which genes are turned off or “silenced” through chemical modifications to the DNA or histone proteins, such as DNA methylation or histone deacetylation. In some forms of narcolepsy, the gene responsible for producing orexin (hypocretin) is not deleted or mutated but is instead silenced epigenetically, meaning that the orexin neurons are present but unable to produce functional orexin peptides due to these modifications. Our lab studies how epigenetic marks (like DNA methylation) on the orexin gene may reduce its expression, contributing to the dysfunction or absence of orexin signaling in the brain. This type of silencing could explain cases where orexin neurons exist but are non-functional due to being epigenetically repressed.
Reversing Epigenetic Silencing
A significant area of research in the lab involves exploring ways to reverse this epigenetic silencing to restore orexin production. This includes:
Pharmacological Approaches
We investigate drugs that target the enzymes responsible for adding or removing epigenetic marks. For instance, DNA methyltransferase inhibitors or histone deacetylase inhibitors may be used to reduce the epigenetic silencing of the orexin gene, allowing the neurons to resume orexin production.
Gene Editing and Epigenetic Editing Tools
We also explore cutting-edge epigenetic editing techniques, such as using CRISPR-dCas9 systems that are designed not to cut DNA but to alter its epigenetic marks, potentially reactivating the silenced orexin gene.
Mechanistic Understanding
By studying the exact mechanisms through which the orexin gene becomes epigenetically silenced, our lab aims to uncover new targets for interventions. This includes identifying specific regions of the orexin gene that are most susceptible to epigenetic modifications and the factors that regulate this process.
If successful, the reversal of epigenetic silencing of the orexin gene could lead to new therapeutic strategies for treating narcolepsy and related disorders. Rather than replacing orexin or compensating for its loss, these strategies aim to reactivate the body’s own orexin production, potentially offering a more natural and lasting treatment. This research represents a novel approach to addressing orexin deficiency, focusing on restoring function at the gene regulation level rather than directly targeting the symptoms.
iPSC-Derived Orexin Neurons
Our lab has made a significant advancement by generating the first induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived orexin neurons from narcolepsy patients. This development offers a powerful tool for studying the mechanisms underlying narcolepsy, particularly the loss of orexin neurons, which is a hallmark of the disorder.
Generation of iPSC-Derived Orexin Neurons
The process begins by obtaining iPSCs from narcolepsy patients. These are stem cells that are created by reprogramming a patient’s skin or blood cells to return them to a pluripotent state, meaning they have the potential to develop into any cell type in the body. We then differentiate these iPSCs into orexin-producing neurons, which mimic the orexin neurons found in the human hypothalamus.
This method allows us to generate patient-specific orexin neurons, providing a model of narcolepsy that captures the exact genetic and molecular background of individuals with the disorder. This is particularly important because the loss of orexin neurons is considered one of key features in narcolepsy type 1, and until now, it has been difficult to study the processes that lead to this neuronal loss in human cells.
Applications for Studying Narcolepsy Processes
Modeling Neuronal Loss
By generating orexin neurons from narcolepsy patients, the lab can observe the cellular and molecular mechanisms that may lead to the degeneration or dysfunction of these neurons. This includes studying epigenetic changes, protein misfolding, or immune-mediated processes that could contribute to neuron loss in narcolepsy.
Drug Testing and Therapeutic Development
These patient-derived neurons provide a valuable platform for testing potential therapies aimed at preventing or reversing orexin neuron loss. Drugs or gene therapies can be screened to determine their effectiveness in protecting orexin neurons or restoring their function.
Personalized Medicine
Since the orexin neurons are derived from patients’ own cells, this model enables personalized approaches to treatment. Researchers can study how different genetic backgrounds affect the progression of narcolepsy and the response to various treatments, paving the way for individualized therapies.
Immune System Involvement
There is evidence that autoimmune mechanisms may contribute to the destruction of orexin neurons in narcolepsy. The iPSC-derived orexin neurons allow researchers to explore how the immune system interacts with these neurons, potentially identifying new pathways involved in the disease.
The ability to generate orexin neurons from iPSCs provides a groundbreaking tool for understanding the pathophysiology of narcolepsy at a cellular level. By recreating orexin neuron loss in a dish, the Vassalli lab can explore previously inaccessible mechanisms and develop targeted therapies aimed at mitigating or curing the disorder. This research could lead to a deeper understanding of not only narcolepsy but also other sleep and neurodegenerative disorders where specific neuron populations are lost.
Optogenetics Approaches
Our lab utilizes optogenetics as a powerful tool to investigate the neural circuits involved in sleep regulation, energy balance, and the functions of specific neuronal populations, particularly in the hypothalamus. This technique allows us to control neuronal activity with high precision using light, enabling us to dissect the roles of different neurons in various physiological processes.
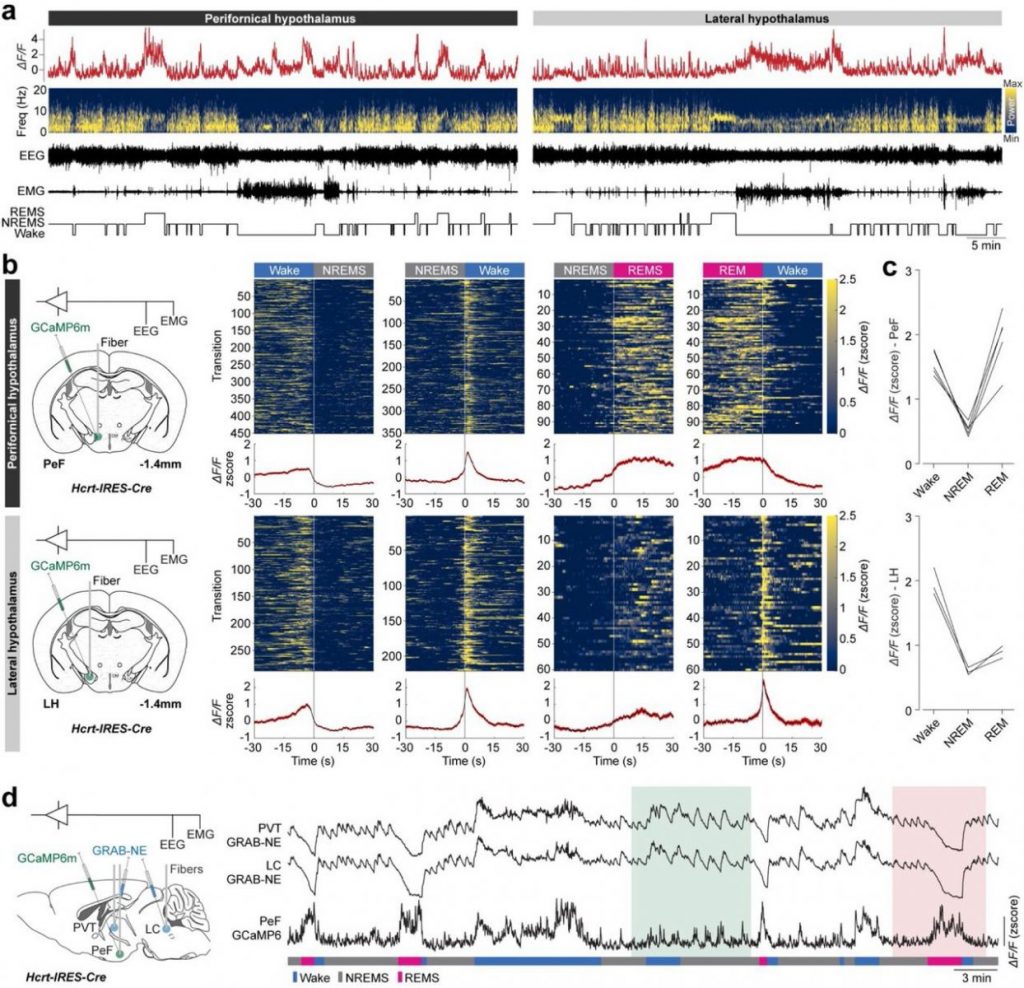
How do we apply optogenetics?
Targeting Specific Neuron Populations
Our lab employs genetically modified mouse models that express light-sensitive proteins, such as channelrhodopsins, in specific types of neurons (e.g., orexin or GABAergic neurons). This allows for the selective activation or inhibition of these neurons in response to light, enabling the study of their specific contributions to behaviors and physiological processes.
Manipulating Sleep-Wake States
By using optogenetic techniques, the lab investigates how the activation or inhibition of orexin neurons influences sleep and wakefulness. For example, stimulating orexin neurons during specific phases of the sleep-wake cycle can help determine their role in promoting arousal and preventing excessive daytime sleepiness.
Studying Neural Circuits
Optogenetics enables our lab to map and manipulate complex neural circuits within the hypothalamus and other brain regions. By activating or silencing specific neuron populations, our can observe how these manipulations affect overall circuit activity and behavior. This helps elucidate the interactions between different types of neurons and their collective impact on sleep regulation and energy balance.
Investigating Behavioral Outcomes
Our lab uses optogenetics to study how changes in neuronal activity affect various behaviors, such as feeding, motivation, and emotional responses. By controlling neuron activity in real time, we can observe the immediate effects on behavior, providing insights into the functional roles of specific neuronal populations.
Applications in Sleep Disorders
The insights gained from optogenetic studies in the lab have implications for understanding sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy. By elucidating how orexin neurons regulate sleep and wakefulness, we aim to identify potential therapeutic targets for restoring normal sleep patterns in individuals with these disorders.
The use of optogenetics in the Vassalli lab continues to evolve, with ongoing research aimed at refining techniques and expanding their applications. This includes exploring the use of more advanced optogenetic tools that allow for the modulation of neuronal activity with greater temporal and spatial precision. As the lab uncovers the intricate roles of specific neuronal populations in sleep regulation and energy balance, optogenetics remains a crucial method for advancing our understanding of neural circuits and their implications for health and disease.